

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Metal carbonyl basicity
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
ص556-557
2025-10-02
110
Metal carbonyl basicity
Key points: Most organometallic carbonyl compounds can be protonated at the metal centre; the acid ity of the protonated form depends on the other ligands on the metal. Many organometallic compounds can be protonated at the metal centre. Metal carbonylates provide many examples of this basicity:
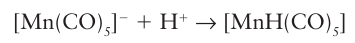
The affinity of metal carbonylates for the proton varies widely (Table 22.6). It is ob- served that, the greater the electron density on the metal centre of the anion, the higher its Brønsted basicity and hence the lower the acidity of its conjugate acid (the metal carbonyl hydride). As we noted in Section 22.7, d-block MH complexes are commonly referred to as ‘hydrides’, which reflects the assignment of oxidation number 1 to an H atom attached to a metal atom. Nevertheless, most of the carbonyl hydrides of metals to the right of the d block are Brønsted acids. The Brønsted acidity of a metal carbonyl hydride is a reflection of the π-acceptor strength of a CO ligand, which stabilizes the conjugate base. Thus, [CoH (CO)4] is acidic whereas [CoH (PMe3)4] is strongly hydridic. In striking contrast to p-block hydrogen compounds, the Brønsted acidity of d-block MH compounds decreases on descending a group. Neutral metal carbonyls (such as pentacarbonyl iron, [Fe (CO)5]) can be protonated in air-free concentrated acid; the Brønsted basicity of a metal atom with oxidation number zero is associated with the presence of nonbonding d electrons. Compounds having metal-metal bonds, such as clusters (Section 22.20), are even more easily protonated; here the Brønsted basicity is associated with the ready protonation of MM bonds to produce a formal 3c,2e bond like that in diborane:
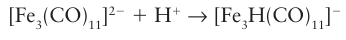
The MHM bridge is by far the most common bonding mode of hydrogen in clusters. Metal basicity is turned to good use in the synthesis of a wide variety of organometallic compounds. For example, alkyl and acyl groups can be attached to metal atoms by the reaction of an alkyl or acyl halide with an anionic metal carbonyl:
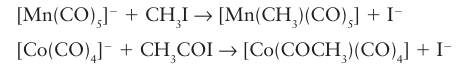
A similar reaction with organometallic halides may be used to form MM bonds:
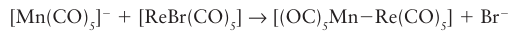
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















