

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Disulfides
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
ص464-465
2025-09-24
53
Disulfides
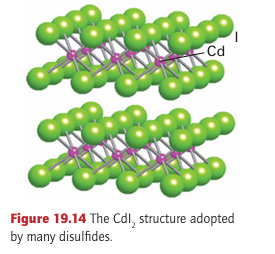
Key points: The 4d- and 5d-series metals often form disulfides with alternating layers of metal ions and sulfide ions; binary disulfides of the early d metals often have a layered structure, whereas Fe2+ and many of the later d-metal disulfides contain discrete S2-2 ions. The disulfides of the d metals fall into two broad classes (Table 19.7). One class consists of layered compounds with either the CdI2 or the MoS2 structure; the other consists of compounds containing discrete S2-2 groups, the pyrites and marcasite structures. The layered disulfides are built from a sulfide layer, a metal layer, and then another sulfide layer (for example, Fig. 19.14). These sandwiches stack together in the crystal with sulfide layers in one slab adjacent to a sulfide layer in the next. Clearly, this crystal
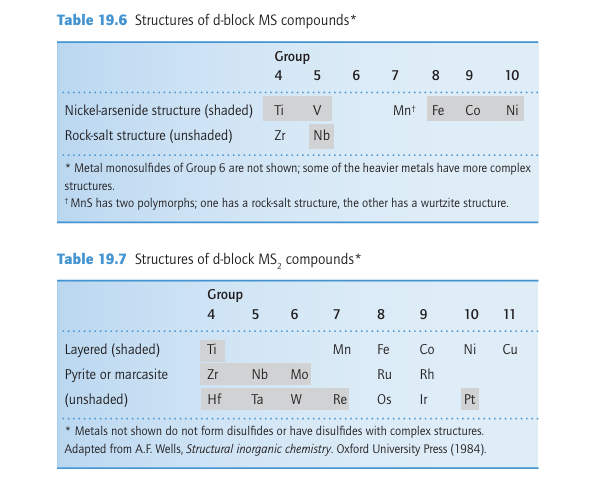
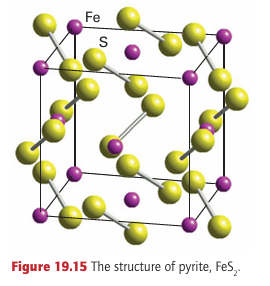
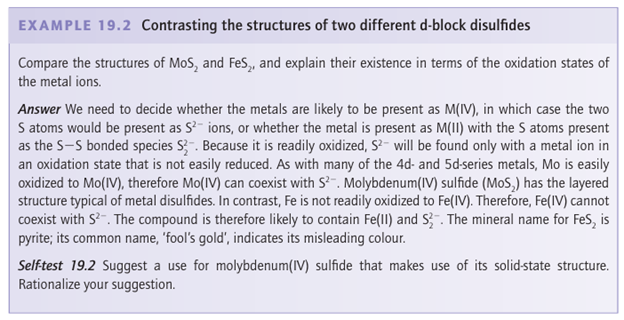
structure is not consistent with a simple ionic model and its formation is a sign of covalence in the bonds between the soft sulfide ion and d-metal cations. The metal ion in these layered structures is surrounded by six S atoms. Its coordination environment is octahedral in some cases (such as PtS2 , which adopts the CdI2 structure shown in Fig. 19.14) and trigonal prismatic in others (MoS2). The layered MoS2 structure is favoured by S-S bonding as indicated by short S-S distances within each of the MoS2 slabs. The common occurrence of the trigonal-prismatic structure in many of these compounds is in striking contrast to the isolated metal complexes, where the octahedral arrangement of ligands is by far the most common. Some of the layered metal sulfides readily undergo intercalation reactions in which ions or molecules penetrate between adjacent sulfide layers (Section 24.10). Compounds containing discrete S2 2 ions adopt the pyrite or marcasite structure (Fig. 19.15). The stability of the formal S2-2 ion in metal sulfides is much greater than that of the O2-2 ion in peroxides, and there are many more metal sulfides in which the anion is S2-2 than there are peroxides.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















