
Molecular interactions
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins، Julio de Paula
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins، Julio de Paula
 المصدر:
ATKINS PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
المصدر:
ATKINS PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
 الجزء والصفحة:
14
الجزء والصفحة:
14
 2025-10-29
2025-10-29
 38
38
Molecular interactions
Real gases show deviations from the perfect gas law because molecules interact with one another. Repulsive forces between molecules assist expansion and attractive forces assist compression. Repulsive forces are significant only when molecules are almost in contact: they are short-range interactions, even on a scale measured in molecular diameters (Fig. 1.13). Because they are short-range interactions, repulsions can be expected to be important only when the average separation of the molecules is small. This is the case at high pressure, when many molecules occupy a small volume. On the other hand, attractive intermolecular forces have a relatively long range and are effective over several molecular diameters. They are important when the molecules are fairly close together but not necessarily touching (at the intermediate separations in Fig. 1.13). Attractive forces are ineffective when the molecules are far apart (well to the right in Fig. 1.13). Intermolecular forces are also important when the temperature is so low that the molecules travel with such low mean speeds that they can be captured by one another. At low pressures, when the sample occupies a large volume, the molecules are so far apart for most of the time that the intermolecular forces play no significant role, and the gas behaves virtually perfectly. At moderate pressures, when the average separation of the molecules is only a few molecular diameters, the attractive forces dominate the repulsive forces. In this case, the gas can be expected to be more compressible than a perfect gas because the forces help to draw the molecules together. At high pressures, when the average separation of the molecules is small, the repulsive forces dominate and the gas can be expected to be less compressible because now the forces help to drive the molecules apart.
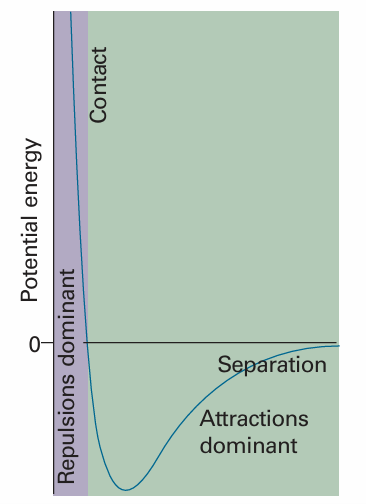
Fig. 1.13 The variation of the potential energy of two molecules on their separation. High positive potential energy (at very small separations) indicates that the interactions between them are strongly repulsive at these distances. At intermediate separations, where the potential energy is negative, the attractive interactions dominate. At large separations (on the right) the potential energy is zero and there is no interaction between the molecules.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


