


 9:2:14
9:2:14  2018-12-12
2018-12-12  1412
1412
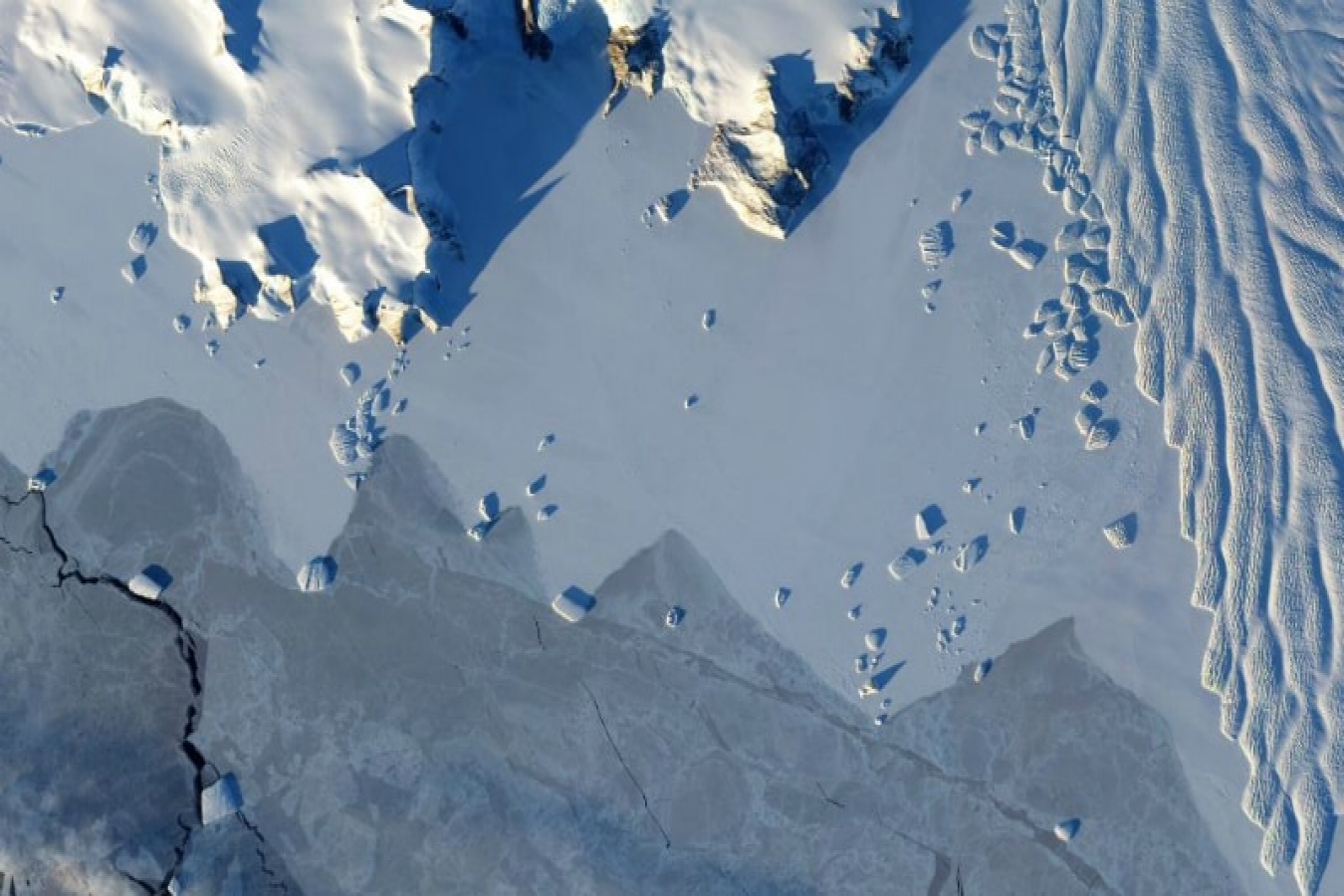

A group of glaciers spanning one-eighth of East Antarctica's coast have begun to lose ice over the past decade, hinting at widespread changes in the ocean, NASA scientists have found.
While East Antarctica has the potential to reshape coastlines around the world through sea level rise, scientists have long considered it more stable than West Antarctica.
The findings, led by Catherine Walker, a glaciologist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Centre in Maryland, revealed that a group of four glaciers sitting to the west of Totten - the biggest glacier in East Antarctica that contains enough ice to raise sea levels by at least 11 feet were losing ice.
Besides these, a handful of smaller glaciers farther east, are also melting away.
The four glaciers west of Totten, in an area called Vincennes Bay, lowered their surface height by about nine feet (about 2.74 metres) since 2008. Before 2008, there had been no measured change in elevation for these glaciers.
Farther east, a collection of glaciers along the Wilkes Land coast have approximately doubled their rate of lowering since around 2009, and their surface is now going down by about 0.8 feet (around 0.24 metres) every year.
These levels of ice loss are small when compared to those of glaciers in West Antarctica. But still, they speak of nascent and widespread change in East Antarctica.
The reason could be recent changes in winds and sea ice have resulted in an increase to the heat delivered by the ocean waters to the glaciers in Wilkes Land and Vincennes Bay, Walker said in a statement on Monday.
"Those two groups of glaciers drain the two largest sub-glacial basins in East Antarctica, and both basins are grounded below sea level," Walker said.
"If warm water can get far enough back, it can progressively reach deeper and deeper ice. This would likely speed up glacier melt and acceleration, but we don't know yet how fast that would happen.
"Still, that's why people are looking at these glaciers, because if you start to see them picking up speed, that suggests that things are destabilising," Walker explained.
The results were presented at the American Geophysical Union meeting in Washington.
Reality Of Islam |
|

MXenes are
A newly dev

Get ready f

Researchers
 9:3:43
9:3:43
 2018-11-05
2018-11-05
10 benefits of Marriage in Islam
 7:5:22
7:5:22
 2019-04-08
2019-04-08
benefits of reciting surat yunus, hud &
 9:45:7
9:45:7
 2018-12-24
2018-12-24
advantages & disadvantages of divorce
 11:35:12
11:35:12
 2018-06-10
2018-06-10
 6:0:51
6:0:51
 2018-10-16
2018-10-16
 4:2:19
4:2:19
 2022-10-10
2022-10-10
 7:59:14
7:59:14
 2018-06-21
2018-06-21
 7:26:19
7:26:19
 2022-04-08
2022-04-08
 5:58:12
5:58:12
 2021-12-18
2021-12-18
al-hussain (peace be upon him)
 10:18:1
10:18:1
 2022-09-21
2022-09-21
 8:15:37
8:15:37
 2023-02-16
2023-02-16
 2:34:48
2:34:48
 2022-01-18
2022-01-18
 5:41:46
5:41:46
 2023-03-18
2023-03-18
| LATEST |