


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 3-1-2022
Date: 10-11-2021
Date: 22-11-2021
|
Mechanism of Glucagon
Glucagon binds to high-affinity G protein–coupled receptors (GPCR) on the cell membrane of hepatocytes. The GPCR for glucagon is distinct from the GPCR that bind epinephrine. [Note: Glucagon receptors are not found on skeletal muscle.] Glucagon binding results in activation of adenylyl cyclase in the plasma membrane (Fig. 1). This causes a rise in cyclic AMP (cAMP), which, in turn, activates cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and increases the phosphorylation of specific enzymes or other proteins. This cascade of increasing enzymic activities results in the phosphorylation-mediated activation or inhibition of key regulatory enzymes involved in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
[Note: Glucagon, like insulin, affects gene transcription. For example, glucagon induces expression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase.]
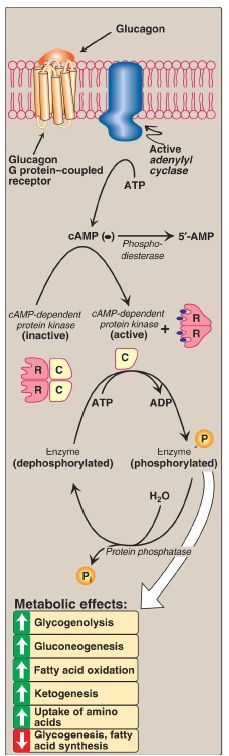
Figure 1: Mechanism of action of glucagon. [Note: For clarity, G-protein activation of adenylyl cyclase has been omitted.] R = regulatory subunit; C = catalytic subunit; cAMP = cyclic adenosine monophosphate; ADP = adenosine diphosphate; = phosphate.

|
|
|
|
مقاومة الأنسولين.. أعراض خفية ومضاعفات خطيرة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمل جديد في علاج ألزهايمر.. اكتشاف إنزيم جديد يساهم في التدهور المعرفي ؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تجري القرعة الخاصة بأداء مناسك الحج لمنتسبيها
|
|
|