


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 12-12-2021
Date: 30-10-2021
Date: 6-12-2021
|
Intestinal Disaccharidases
The final digestive processes occur primarily at the mucosal lining of the duodenum and upper jejunum and include the action of several disaccharidases ( Fig. 1). For example, isomaltase cleaves the α(1→6) bond in isomaltose, and maltase cleaves the α(1→4) bond in maltose and maltotriose, each producing glucose. Sucrase cleaves the α(1→2) bond in sucrose, producing glucose and fructose, and lactase (β-galactosidase) cleaves the β(1→4) bond in lactose, producing galactose and glucose. [Note: The substrates for isomaltase are broader than its name suggests, and it hydrolyzes the majority of maltose.] Trehalose, an α(1→1) disaccharide of glucose found in mushrooms and other fungi, is cleaved by trehalase. These enzymes are transmembrane proteins of the brush border on the luminal (apical) surface of the enterocytes.
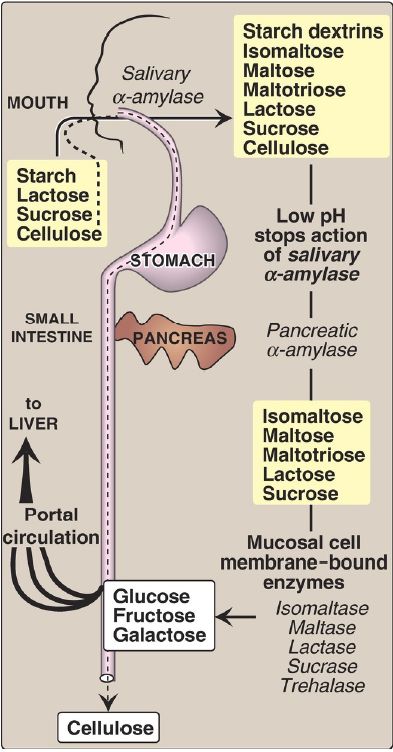
Figure 1: Digestion of carbohydrates. [Note: Indigestible cellulose enters the colon and is excreted.]
Sucrase and isomaltase are enzymic activities of a single protein that is cleaved into two functional subunits, which remain associated in the cell membrane and form the sucrase-isomaltase (SI) complex. In contrast, maltase is one of two enzymic activities of the single membrane protein maltase-glucoamylase (MGA) that does not get cleaved. Its second enzymic activity, glucoamylase, cleaves α(1→4) glycosidic bonds in dextrins.

|
|
|
|
مقاومة الأنسولين.. أعراض خفية ومضاعفات خطيرة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمل جديد في علاج ألزهايمر.. اكتشاف إنزيم جديد يساهم في التدهور المعرفي ؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تجري القرعة الخاصة بأداء مناسك الحج لمنتسبيها
|
|
|