

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Kingdom Monera
المؤلف:
National Council of Educational Research and Training
المصدر:
Biology
الجزء والصفحة:
29-1-2021
4437
Kingdom Monera
Bacteria are the sole members of the Kingdom Monera. They are the most abundant micro-organisms. Bacteria occur almost everywhere. Hundreds of bacteria are present in a handful of soil. They also live in extreme habitats such as hot springs, deserts, snow and deep oceans where very few other life forms can survive. Many of them live in or on other organisms as parasites.
Bacteria are grouped under four categories based on their shape: the spherical Coccus (pl.: cocci), the rod-shaped Bacillus (pl.: bacilli), the comma-shaped Vibrium (pl.: vibrio) and the spiral Spirillum (pl.: spirilla) (Figure 1).
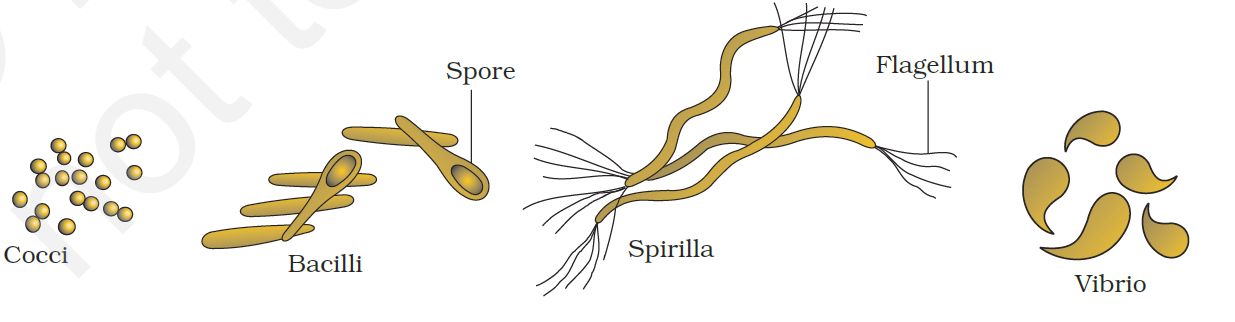
Figure1. Bacteria of different shapes
Though the bacterial structure is very simple, they are very complex in behaviour. Compared to many other organisms, bacteria as a group show the most extensive metabolic diversity. Some of the bacteria are autotrophic, i.e., they synthesise their own food from inorganic substrates. They may be photosynthetic autotrophic or chemosynthetic autotrophic. The vast majority of bacteria are heterotrophs, i.e., they do not synthesise their own food but depend on other organisms or on dead organic matter for food.
1.1 Archaebacteria
These bacteria are special since they live in some of the most harsh habitats such as extreme salty areas (halophiles), hot springs (thermoacidophiles) and marshy areas (methanogens). Archaebacteria differ from other bacteria in having a different cell wall structure and this feature is responsible for their survival in extreme conditions. Methanogens are present in the gut of several ruminant animals such as cows and buffaloes and they are responsible for the production of methane (biogas) from the dung of these animals.
1.2 Eubacteria
There are thousands of different eubacteria or ‘true bacteria’. They are characterised by the presence of a rigid cell wall, and if motile, a flagellum. The cyanobacteria (also referred to as blue-green algae) have chlorophyll a similar to green plants and are photosynthetic autotrophs (Figure 2.). The cyanobacteria are unicellular, colonial or filamentous, freshwater/marine or terrestrial algae. The colonies are generally surrounded by gelatinous sheath. They often form blooms in polluted water bodies. Some of these organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts, e.g., Nostoc and Anabaena. Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria oxidise various inorganic substances such as nitrates, nitrites and ammonia and use the released energy for their ATP production. They play a great role in recycling nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous, iron and sulphur.
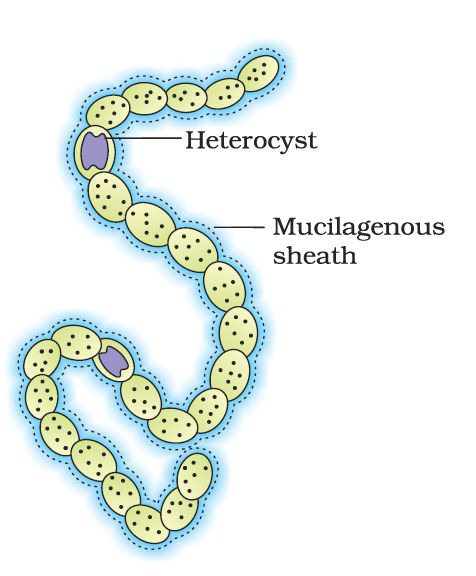
Figure 2. A filamentous blue-green algae – Nostoc
Heterotrophic bacteria are the most abundant in nature. The majority are important decomposers. Many of them have a significant impact on human affairs. They are helpful in making curd from milk, production of antibiotics, fixing nitrogen in legume roots, etc. Some are pathogens causing damage to human beings, crops, farm animals and pets. Cholera, typhoid, tetanus, citrus canker are well known diseases caused by different bacteria. Bacteria reproduce mainly by fission (Figure .3). Sometimes, under unfavourable conditions, they produce spores. They also reproduce by a sort of sexual reproduction by adopting a primitive type of DNA transfer from one bacterium to the other.
The Mycoplasma are organisms that completely lack a cell wall. They are the smallest living cells known and can survive without oxygen. Many mycoplasma are pathogenic in animals and plants.
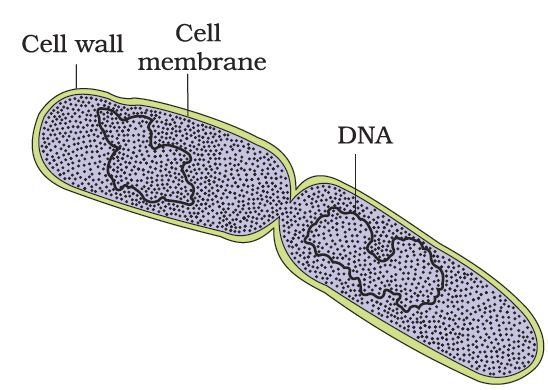
Figure 3. A dividing bacterium
 الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
الاكثر قراءة في الأحياء العامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















