

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Coenzyme Regeneration
المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
الجزء والصفحة:
9-1-2021
2399
Coenzyme Regeneration
Around 25% of enzymes are oxidoreductases and they catalyse many reactions that are of great interest to biotechnologists.
However, most of these enzymes require participation of a coenzyme such as NAD, NADH, NADP, NADPH or ATP. Coenzymes are chemically changed during reaction and so in effect become an expensive consumable. Hence efficient regeneration of coenzyme is essential
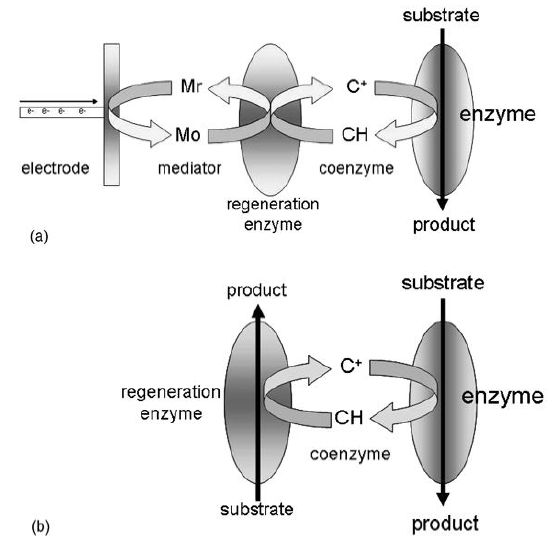
Figure 1. Diagram depicting coenzyme regeneration using (a) an electrode, regeneration enzyme and chemical mediator (Mr, reduced; Mo, oxidised) to recycle the coenzyme and (b) a regeneration enzyme in a reaction that utilises a secondary substrate.
for applications that utilise these enzymes. There are basically two mechanisms to regenerate coenzyme, as depicted in Figure 1. In the first method (Figure 1a), the coenzyme is regenerated electrochemically using electrons supplied from an electrode. To improve efficiency, a regeneration enzyme and chemical mediators are added to more effectively interact with the electrode. The second method (Figure 1b) does not use an electrode and instead uses a second enzyme that catalyses a reverse reaction to regenerate coenzyme. Use of a second enzyme reaction requires close coupling of the reaction kinetics of the secondary enzyme to match that of the primary enzyme reaction.
For example, if the rate of catalysis of the primary reaction is 500 mmol min-1 and the secondary enzyme catalyses at a rate of 200 mmol min-1, then the slower reaction will drag the primary reaction and lower the efficiency. On the other hand, if the secondary reaction is too fast (e.g. 2000 mmol min-1), then there would be inefficient and uneconomical waste of material. There are enzymes available that have been adapted for coenzyme regeneration to improve the efficiency of the process.
Many attempts have been made to immobilise coenzymes and enzymes together to try to produce a universal efficient biocatalytic system with continuous coenzyme regeneration and, although some systems work well, further innovation is still required to produce a fully efficient and effective system that will realise the full potential of all the valuable enzymes that have coenzyme requirements.
 الاكثر قراءة في الانزيمات
الاكثر قراءة في الانزيمات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















