

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Enzyme Immunoassay
المؤلف:
Mary Louise Turgeon
المصدر:
Immunology & Serology in Laboratory Medicine
الجزء والصفحة:
5th E, P161-162
2025-07-17
59
There are two general approaches to diagnosing condition, dis eases or conditions by immunoassay, testing for specific antigens or for antigen-specific antibodies. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), also known as an enzyme immunoassay (EIA), is designed to detect antigens or antibodies by producing an enzyme-triggered color change.
The EIA method uses a nonisotopic label that offers the advantage of safety. EIA is usually an objective measurement that provides numerical results. Some EIA procedures provide diagnostic information and measure immune status (e.g., detect total antibody IgM or IgG).
The EIA method uses the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantitate immunologic reactions. An enzyme labeled antibody or enzyme-labeled antigen conjugate is used in immunologic assays (Box 1). The enzyme, with its substrate, detects the presence and quantity of antigen or antibody in a patient specimen. In some tissues, an enzyme-labeled antibody can identify antigenic locations.
Box1. Enzyme Immunoassays
Various enzymes are used in enzyme immunoassay (Table 1). Common enzyme labels are horseradish peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and beta-galactosidase. To be used in an EIA, an enzyme must fulfill the following criteria:
• High degree of stability
• Extreme specificity
• Absence from the antigen or antibody
• No alteration by inhibitor within the system
In a representative EIA test, a plastic bead or plastic plate is coated with antigen (e.g., virus; Fig. 1). The antigen reacts with antibody in the patient’s serum. The bead or plate is then incubated with an enzyme-labeled antibody conjugate. If anti body is present, the conjugate reacts with the antigen-antibody complex on the bead or plate. The enzyme activity is measured spectrophotometrically after the addition of the specific chromogenic substrate. For example, peroxidase cleaves its substrate, o-dianisidine, causing a color change. In some cases, the test can be read subjectively.
Table1. Enzymes Used in Enzyme Immunoassays
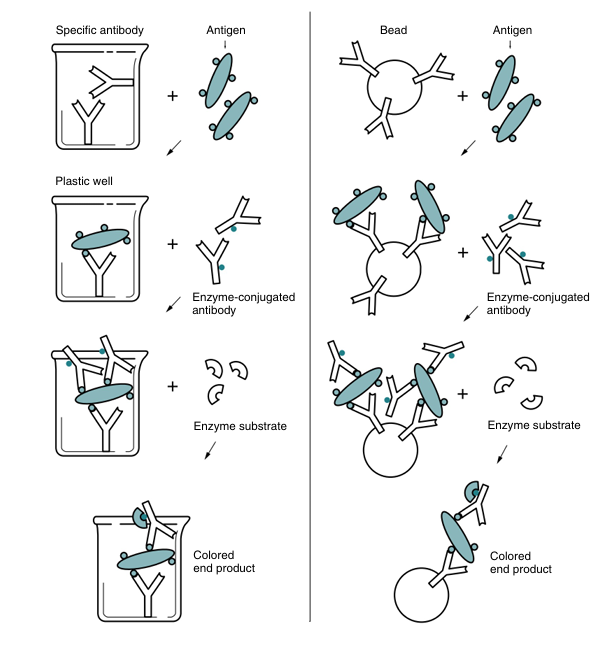
Fig1. Principle of solid phase enzyme immunosorbent assay. (From Forbes BA, Sahm DF, Weissfeld AS: Bailey and Scott’s diagnostic microbiology, ed 12, St Louis, 2007, Mosby.)
The results of a typical test are calculated by comparing the spectrophotometric reading of the patient’s serum to that of a control or reference serum. The advantage of an objective enzyme test is that results are not dependent on a technician’s interpretations. In general, the EIA procedure is faster and requires less laboratory work than comparable methods.
Antigen Detection
EIAs for antigen detection (e.g., hepatitis B surface antigen [HBsAg]) have four steps. Antigen-specific antibody is attached to a solid-phase surface (e.g., plastic beads). The patient’s serum that may contain the antigen is added. Next, an enzyme-labeled antibody specific to the antigen (conjugate) is added. Finally, a chromogenic substrate is added, which changes color in the presence of the enzyme. The amount of color that develops is proportional to the amount of antigen in the patient specimen.
Antibody Detection
There are three types of EIAs for antibody detection—noncompetitive, competitive, and capture.
Noncompetitive Enzyme Immunoassay
The noncompetitive enzyme immunoassay takes place when a specific antigen is attached to a solid-phase surface, such as a plastic bead or microtiter well. The patient’s serum that could contain antibody (e.g., cytomegalovirus [CMV] immunoglobulin G [IgG], HIV antibody) is added to the solid-phase sur face, followed by an enzyme-labeled antibody specific to the test antibody. The added chromogenic substrate changes color if the enzyme is present. The amount of color that develops is proportional to the amount of antibody in the patient’s serum.
Competitive Enzyme Immunoassay
Competitive enzyme immunoassay involves using a solid phase surface to which specific antigen is attached. The patient’s potentially containing antibody (e.g., hepatitis B core anti body) and an enzyme-labeled antibody specific to the test anti body (conjugate) are mixed. Chromogenic substrate is then added, which changes color in the presence of the enzyme. The amount of color that develops is inversely proportional to the amount of antibody in the patient’s serum.
Capture Enzyme Immunoassay
Capture enzyme immunoassay is designed to detect a specific type of antibody, such as IgM or IgG, CMV IgM, rubella IgM, or Toxoplasma IgM. Antibody specific for IgM or IgG is attached to a solid-phase surface (plastic bead, microtiter well). The patient specimen potentially containing IgM or IgG is added. Specific antigen is then added. Finally, chromogenic substrate is added, which changes color in the presence of the enzyme. The amount of color that develops is proportional to the amount of antigen-specific IgM or IgG in the patient’s serum.
 الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















