

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous

Past Simple


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous

Passive and Active


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology


Semantics


Pragmatics

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies
MalE – global change
المؤلف:
Loga Baskaran
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
1037-61
2024-06-14
978
MalE – global change
Although previous studies of MalE closely linked it to Singapore English (SgE), it is now appropriate to divorce them from each other at least on two historical considerations. Firstly, since 1965 Singapore is no longer in any way politically connected to Malaya or Malaysia; the case for sociolinguistic differentiation over 40 years is therefore reasonably strong. Secondly, the language policies in both nations have been different for the past 40 years. This will have varied implications on the role and long-term effects of English on the local populace of each nation. Tongue (1974), who describes the English of Singapore and Malaysia (ESM), predicted that within a hundred years the idea of one ‘ESM’ would become inapplicable. In linguistic terms, there are significant differences in substrate too. Chinese varieties predominate in Singapore, but are a minority in Malaysia. The implications of this difference have yet to be researched.
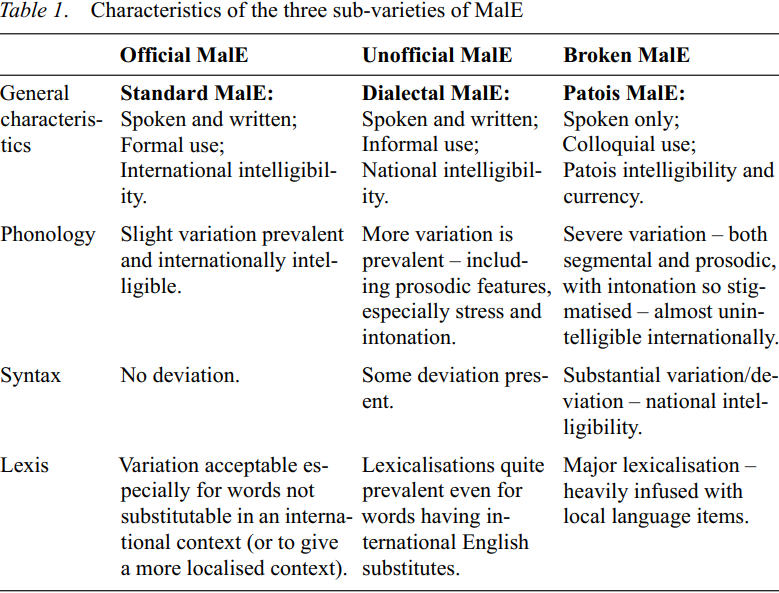
Many researchers have described ‘ESM’ in terms of a standard and colloquial form with various terms like ‘standard’, ‘informal’, ‘uneducated’, ‘low’ and ‘communicative forms’. Platt and Weber (1980), along with Mary Tay (1993). I, too, prefer to take a three-tiered approach to describing MalE although I prefer to use the terms official MalE (standard MalE), Unofficial MalE (dialectal MalE) and Broken MalE (patois MalE). Thus the basic subdivision in my description of MalE would be as tabulated below:
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















