

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Segmental phonology
المؤلف:
Rajend Mesthrie
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
955-55
2024-05-25
1449
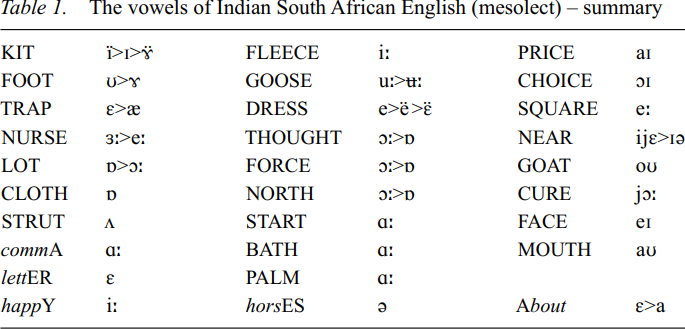
Segmental phonology
InSAfE has been studied mostly as a contact variety that involves a great deal of syntactic variation. If less attention has been paid to its phonetics, it has to do with the paucity of researchers working on the accents of varieties of South African English (SAfE) rather than any intrinsic qualities of InSAfE phonetics. On the contrary, InSAfE holds the promise of subtle variations along the following dimensions:
(a) Five substrate languages belonging to two distinct language families: Dravidian (Tamil, Telugu) and Indo-European (Bhojpuri-Hindi, Gujarati, Urdu, Konkani and Sindhi/Meman dialect);
(b) Links with IndE (the English of India);
(c) Links with South African varieties of English, especially varieties spoken in KwaZulu-Natal;
(d) Emergence of a core InSAfE phonology as younger speakers lose contact with the languages of their grandparents’ generation;
(e) Ongoing acculturation amongst middle-class speakers to “General” and “Cultivated” varieties of SAfE as the rigid barriers between young people of different backgrounds weaken, especially in the post-apartheid schoolgrounds;
(f) Regional variation within InSAfE, involving the main dialect in KwaZulu-Natal and smaller pockets in other provinces – Gauteng, Eastern Cape and Western Cape.
The description below is based on my analysis of tape recordings carried out in the mid-1980s, reported in Mesthrie (1992: 34-43) for fieldwork, (1992:136-141) for phonetics. These have been supplemented by more recent recordings in the late 1990s and early 2000s. In addition I rely on earlier discussions by Bailey (c 1985, unpublished notes), Naidoo (1971) and Bughwan (1970).
 الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















