

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous

Past Simple


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous

Passive and Active


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology


Semantics


Pragmatics

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies
Linking and intrusive /r/
المؤلف:
Clive Upton
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
228-11
2024-03-13
1038
Linking and intrusive /r/
Linking /r/, retained historical post-vocalic word-final /r/ occurring before a vowel in the following word, is, as stated above at lettER, a normal feature of Received Pronunciation. In the most careful, mannered forms this might be avoided, rendering far away 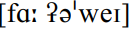 rather than
rather than 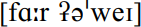 : it is unlikely that many speakers feel under special pressure to avoid such an hiatus now.
: it is unlikely that many speakers feel under special pressure to avoid such an hiatus now.
The insertion of a non-historical intrusive /r/, referred to in commA above, when following word-final 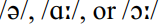 before a word beginning with a vowel, has typically been proscribed for users of Received Pronunciation. This creates an hiatus between the adjacent vowel sounds or, alternatively, a glottal plosive might be interposed between them, giving
before a word beginning with a vowel, has typically been proscribed for users of Received Pronunciation. This creates an hiatus between the adjacent vowel sounds or, alternatively, a glottal plosive might be interposed between them, giving 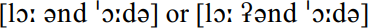 l aw and order. RP shows no such inhibitions, with intrusive /r/ being the norm:
l aw and order. RP shows no such inhibitions, with intrusive /r/ being the norm: 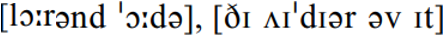 the idea of it. Similarly, intrusive /r/ occurs as the RP norm word-internally where the need is to avoid the hiatus, thus
the idea of it. Similarly, intrusive /r/ occurs as the RP norm word-internally where the need is to avoid the hiatus, thus 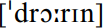 drawing.
drawing.















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)

















