
Finite Size of Nucleus
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 67
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 67
 14-8-2016
14-8-2016
 1668
1668
Finite Size of Nucleus
Regard the nucleus of charge Z as a sphere of radius R0 with a uniform charge density. Assume that R0 << a0 where a0 is the Bohr radius of the hydrogen atom.
a) Derive an expression for the electrostatic potential V(r) between the nucleus and the electrons in the atom. If V0(r) = -Ze2/r is the potential from a point charge, find the difference δV = V(r) – V0(r) due to the size of the nucleus.
b) Assume one electron is bound to the nucleus in the lowest bound state. What is its wave function when calculated using the potential V0(r) from a point nucleus?
c) Use first-order perturbation theory to derive an expression for the change in the ground state energy of the electron due to the finite size of the nucleus.
SOLUTION
a) To find the potential V(r) near the nucleus, we note Gauss’s law, which states that for an electron at a distance r from the center of a spherical charge distribution, the electric field is provided only by those electrons inside a sphere of radius r. For r < R0, this is the charge Z(r/R0)3, whereas for r > R0 it is just the charge Z . Thus, we find for the derivative of the potential energy:
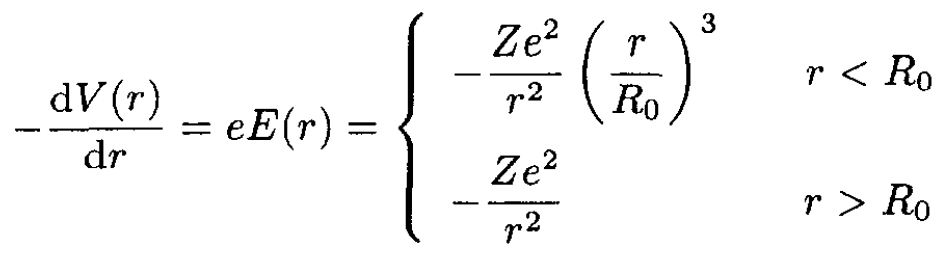 (1)
(1)
where C is a constant of integration. We chose C = -3 to make the potential continuous at r = R0:
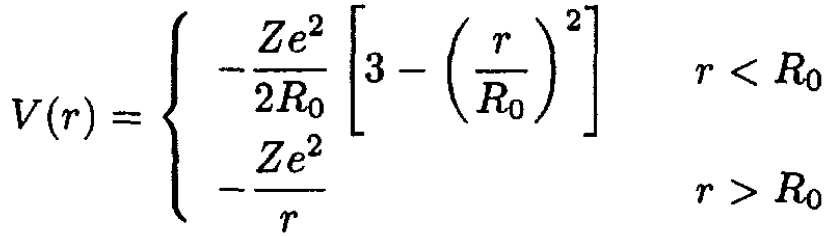 (3)
(3)
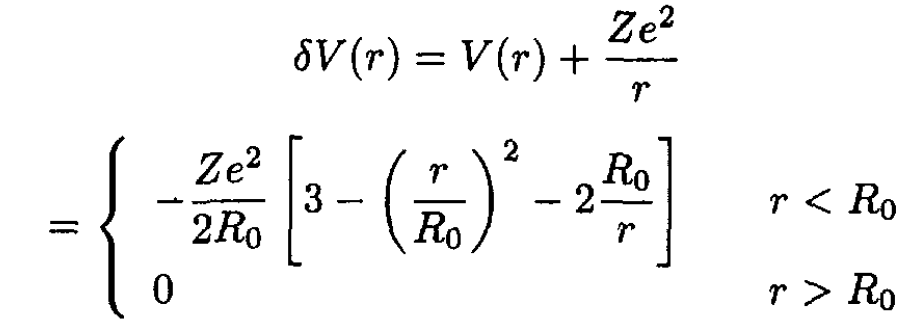 (4)
(4)
b) For a single electron bound to a point nucleus, we can use hydrogen wave functions:
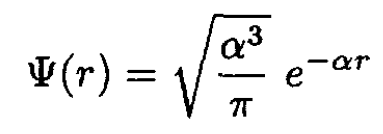 (5)
(5)
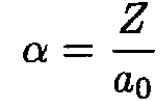 (6)
(6)
c) The first-order change in the ground state wave energy is
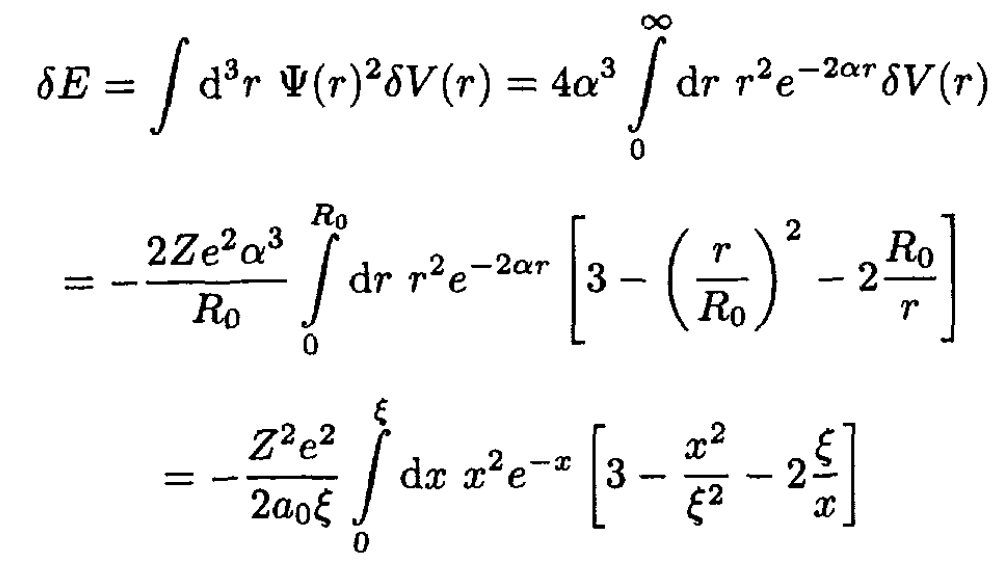 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
For any physical value of Z, the parameter ξ is very much smaller than unity. One can evaluate the above integral as an expansion in ξ and show that the first term is -0.2ξ3, so the answer is approximately 0.2Z2 ERξ2.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


