


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية| Most probable number (MPN) method APHA 2001 and BAM/FDA 2004 for Vibrio parahaemolyticus in foods |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 6-3-2016
Date: 17-3-2016
Date: 13-3-2016
|
Most probable number (MPN) method APHA 2001 and BAM/FDA 2004 for Vibrio parahaemolyticus in foods
Method of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), as described in the May/2004 revision of the Bacteriological Analytical Manual Online (Kaysner and DePaola Jr, 2004) and of the American Public Health Association (APHA), as described in the 4th Ed. of the Compendium of Methods for the Micro-biological Examination of Foods (Kaysner and De Paola Jr., 2001).
1. Material required for analysis
Isolation
• Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS)
• Alkaline Peptone Water (APW)
• Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Sucrose (TCBS) Agar
• Laboratory incubator set to 35 ± 2°C
Screening
• T1N1 Agar (tubes and plates)
• T1N0 Broth (same formulation of T1N1 without NaCl) (tubes)
• T1N3 Broth (same formulation of T1N1 with the NaCl concentration adjusted to 3%) (tubes)
• Motility Test Medium with NaCl concentration adjusted to 3%
• Arginine Glucose Slants (AGS) with 3% NaCl
• Gram Stain Reagents
• Laboratory incubator set to 35 ± 2°C
Confirmation by biochemical tests
• Kit API 20E or equivalent
• Sterile 2% NaCl Solution
• Laboratory incubator set to 35 ± 2°C
2 . Procedure
A general flowchart for the enumeration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in foods using the Most Probable Number (MPN) methods APHA 2001 and BAM/FDA 2004 is shown in Figure 1.
Recommendations for the samples storage: The same described for V. cholerae.
a) Enrichment: homogenize 50 g of sample with 450 ml of Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS). For fishes include the surface tissues, the gills, and the gut. For crustaceans such as shrimp, use the entire animal (if possible) or the central portion including the gill and the gut. For molluscan shellfish pool 12 animals with an equal volume of PBS (1:2 dilution), blend at high speed for 90s and prepare 10−1 dilution by transferring 20 g of the 1:2 homogenate to 80 ml of PBS.
From the homogenized first dilution (10−1) pre-pare the subsequent decimal dilutions and inoculate three 1 ml aliquots of the 10−1, 10−2, 10−3, and 10−4 dilutions into a series of three 10 ml tubes of Alkaline Peptone Water (APW) per dilution. Incubate the tubes at 35 ± 2°C/18–24 h.
Note a1) If the expected V.parahaemolyticus count is low (products heated, dried, or frozen, for example) start the series with three 10 ml aliquots of the 10−1 dilution inoculated into three 10 ml tubes of double strength APW.
b) Selective differential plating: From each APW tube, streak a loopful from the surface pellicle of the broth onto a Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Sucrose (TCBS) Agar plate. Incubate the TSBC plates at 35 ± 2°C/18–24 h.
c) Screening: Select for screening three or more typical colonies from each plate. Typical colonies of V. parahaemolyticus on TCBS are green or bluish (sucrose negative), round and opaque. V. vulnificus colonies are similar and V. alginolyticus colonies are large and yellow (sucrose positive).
Transfer the typical colonies to T1N1 agar slants. Colonies selected from crowded plates should be purified by streaking on T1N1 Agar plates. Incu-bate the T1N1 slants or plates at 35 ± 2°C/over-night and proceed with the screening tests below (from T1N1 plates use a single isolated colony for the tests).
Note c.1) The T1N1 tubes may be substituted for the Motility Test Medium with 2–3% of NaCl and used as inoculum for the screening tests. In this case it is not necessary to repeat the motility test (item c.3).
c.1) Growth on Arginine Glucose Slants (AGS) with 2–3% of NaCl: From the T1N1 cultures inoculate tubes of AGS by streaking the slant and stabbing the butt. Incubate the AGS tubes at 35 ± 2°C/overnight (with the caps slightly loosened). The typical characteristics of V. parahaemolyticus cultures are alkaline (purple) slant and an acid (yellow) butt (arginine not hydrolyzed) without gas or H2S production.
c.2) Salt requirement test: From the T1N1 cultures inoculate tubes of T1N0 and T1N3 broths. Incubate the tubes at 35 ± 2°C/over-night. V. parahaemolyticus cultures grows on T1N3 (3% of NaCl) but does not growth without NaCl on T1N0.
c.3) Gram stain and motility test: From the T1N1 cultures prepare a smear for Gram stain and inoculate a tube of Motility Test Medium (with 2–3% of NaCl) by stabbing. Incubate the Motility Test Medium at 35 ± 2°C/overnight. A circular outgrowth from the line of the stab constitutes a positive test. V. parahaemolyticus is motile Gram negative pleomorphic curved or straight rods.
d) Confirmation: Only motile, Gram-negative rods that produce an acid butt and an alkaline slant on AGS, do not form H2S or gas, and are salt-requiring (do not growth on T1N0) are suspect and require confirmation.
Use the API 20E (BioMérieux) diagnostic strip or an equivalent biochemical kit for the identification and confirmation of the isolates. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and prepare the inoculum suspending a loopful of the culture into a 2% NaCl solution.
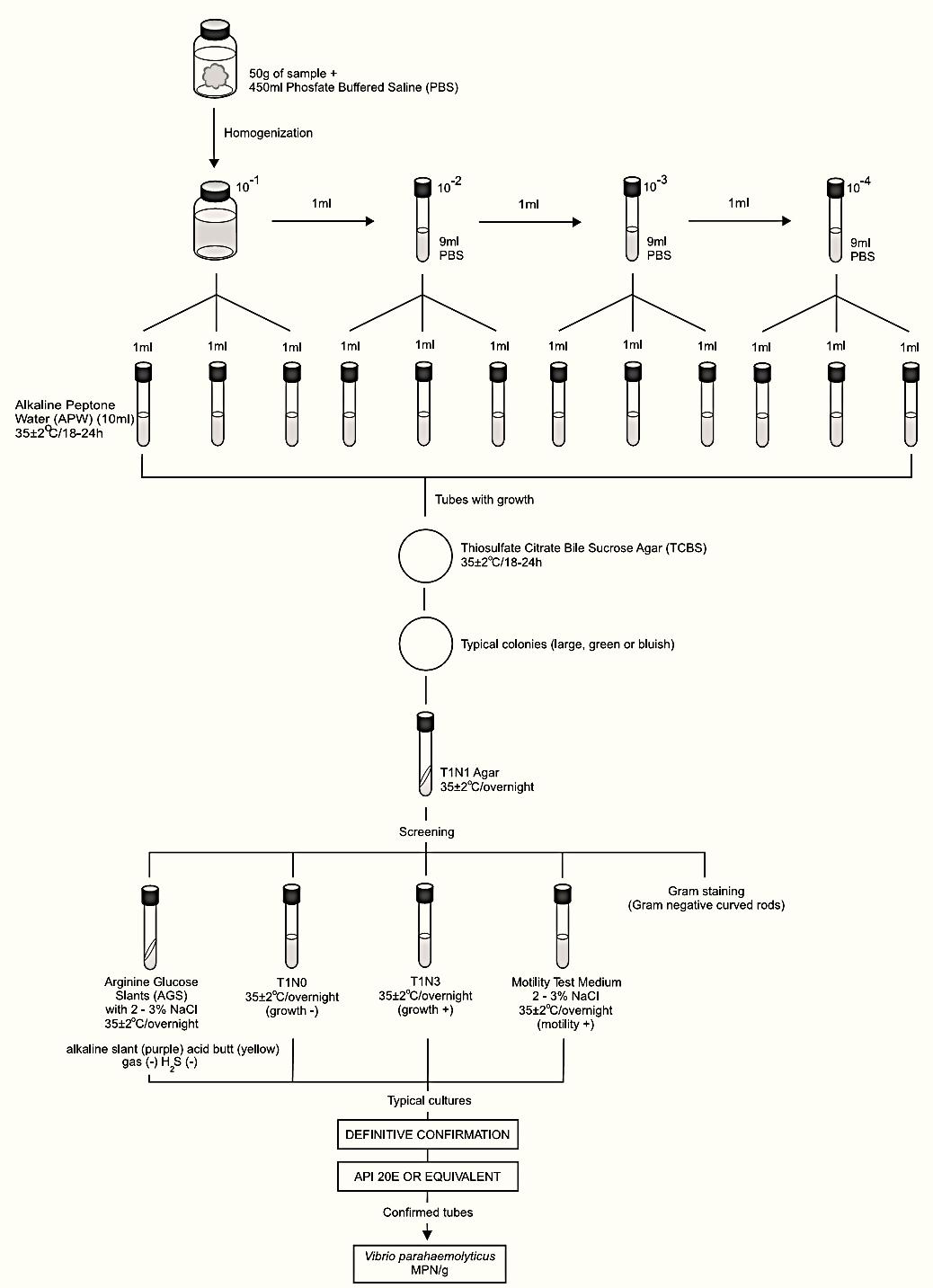
Figure1 Scheme of analysis for the enumeration of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in foods using the Most Probable Number (MPN) methods APHA 2001 and BAM/FDA 2004 (Kaysner and DePaola Jr, 2001, Kaysner and DePaola Jr, 2004).
e) Pathogenicity determination: For these tests it is preferable to send the cultures to a specialist or reference laboratory.
f ) Calculation of the results: From the APW tubes confirmed calculate most probable number (MPN).
References
Silva, N.D .; Taniwaki, M.H. ; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Silveira, N.F.A. , Nasdcimento , M.D.D. and Gomes ,R.A.R .(2013) . Microbiological examination methods of food and water a laboratory Manual. Institute of Food Technology – ITAL, Campinas, SP, Brazil .
Kaysner, C.A & DePaola Jr., A. (2001) Vibrio. In: Downes, F.P. & Ito, K. (eds). Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods. 4th edition. Washington, American Public Health Association. Chapter 40, pp. 405–420.
Kaysner, C.A & DePaola Jr., A. (2004) Vibrio. In: FDA (ed.) Bacteriological Analytical Manual, Chapter 5. [Online] Silver Spring, Food and Drug Administration. Available from: http://www. fda.gov/Food/ScienceResearch/LaboratoryMethods/BacteriologicalAnalyticalManualBAM/ucm070830.htm [Accessed 3rd November 2011].