


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 30-11-2020
التاريخ: 14-3-2021
التاريخ: 2024-03-26
التاريخ: 30-11-2020
|
Now let us discuss the problem of finding the moments of inertia of various objects. The formula for the moment of inertia about the z-axis of an object is
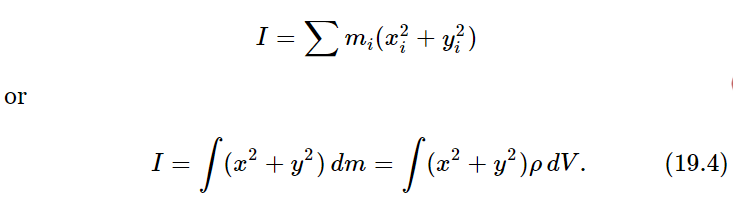
That is, we must sum the masses, each one multiplied by the square of its distance (x2i+y2i) from the axis. Note that it is not the three-dimensional distance, only the two-dimensional distance squared, even for a three-dimensional object. For the most part, we shall restrict ourselves to two-dimensional objects, but the formula for rotation about the z-axis is just the same in three dimensions.
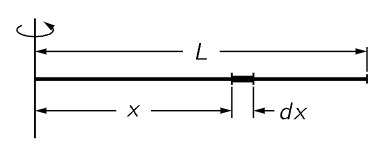
Fig. 19–3. A straight rod of length L rotating about an axis through one end.
As a simple example, consider a rod rotating about a perpendicular axis through one end (Fig. 19–3). Now we must sum all the masses times the x-distances squared (the y’s being all zero in this case). What we mean by “the sum,” of course, is the integral of x2 times the little elements of mass. If we divide the rod into small elements of length dx, the corresponding elements of mass are proportional to dx, and if dx were the length of the whole rod the mass would be M. Therefore
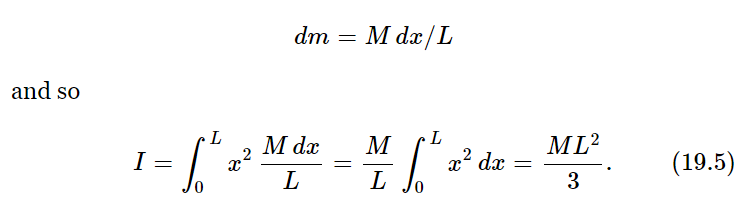
The dimensions of moment of inertia are always mass times length squared, so all we really had to work out was the factor 1/3.
Now what is I if the rotation axis is at the center of the rod? We could just do the integral over again, letting x range from −1/2 L to +1/2 L. But let us notice a few things about the moment of inertia. We can imagine the rod as two rods, each of mass M/2 and length L/2; the moments of inertia of the two small rods are equal, and are both given by the formula (19.5). Therefore, the moment of inertia is

Thus it is much easier to turn a rod about its center, than to swing it around an end.
Of course, we could go on to compute the moments of inertia of various other bodies of interest. However, while such computations provide a certain amount of important exercise in the calculus, they are not basically of interest to us as such. There is, however, an interesting theorem which is very useful. Suppose we have an object, and we want to find its moment of inertia around some axis. That means we want the inertia needed to carry it by rotation about that axis. Now if we support the object on pivots at the center of mass, so that the object does not turn as it rotates about the axis (because there is no torque on it from inertial effects, and therefore it will not turn when we start moving it), then the forces needed to swing it around are the same as though all the mass were concentrated at the center of mass, and the moment of inertia would be simply I1=MR2CM, where RCM is the distance from the axis to the center of mass. But of course, that is not the right formula for the moment of inertia of an object which is really being rotated as it revolves, because not only is the center of it moving in a circle, which would contribute an amount I1 to the moment of inertia, but also, we must turn it about its center of mass. So it is not unreasonable that we must add to I1 the moment of inertia Ic about the center of mass. So, it is a good guess that the total moment of inertia about any axis will be

This theorem is called the parallel-axis theorem, and may be easily proved. The moment of inertia about any axis is the mass times the sum of the xi’s and the yi’s, each squared: I=∑(x2i+y2i) mi. We shall concentrate on the x’s, but of course the y’s work the same way. Now x is the distance of a particular point mass from the origin, but let us consider how it would look if we measured x′ from the CM, instead of x from the origin. To get ready for this analysis, we write
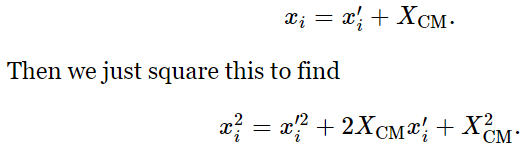
So, when this is multiplied by mi and summed over all i, what happens? Taking the constants outside the summation sign, we get
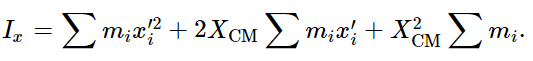
The third sum is easy; it is just MX2CM. In the second sum there are two pieces, one of them is ∑mix′i, which is the total mass times the x′-coordinate of the center of mass. But this contributes nothing, because x′ is measured from the center of mass, and in these axes the average position of all the particles, weighted by the masses, is zero. The first sum, of course, is the x part of Ic. Thus, we arrive at Eq. (19.7), just as we guessed.
Let us check (19.7) for one example. Let us just see whether it works for the rod. For an axis through one end, the moment of inertia should be ML2/3, for we calculated that. The center of mass of a rod, of course, is in the center of the rod, at a distance L/2. Therefore, we should find that ML2/3=ML2/12+M(L/2)2. Since one-quarter plus one-twelfth is one-third, we have made no fundamental error.
Incidentally, we did not really need to use an integral to find the moment of inertia (19.5). If we simply assume that it is ML2 times γ, an unknown coefficient, and then use the argument about the two halves to get 1/4 γ for (19.6), then from our argument about transferring the axes we could prove that γ=1/4 γ+1/4, so γ must be 1/3. There is always another way to do it!
In applying the parallel-axis theorem, it is of course important to remember that the axis for Ic must be parallel to the axis about which the moment of inertia is wanted.
One further property of the moment of inertia is worth mentioning because it is often helpful in finding the moment of inertia of certain kinds of objects. This property is that if one has a plane figure and a set of coordinate axes with origin in the plane and z-axis perpendicular to the plane, then the moment of inertia of this figure about the z-axis is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia about the x- and y-axes. This is easily proved by noting that
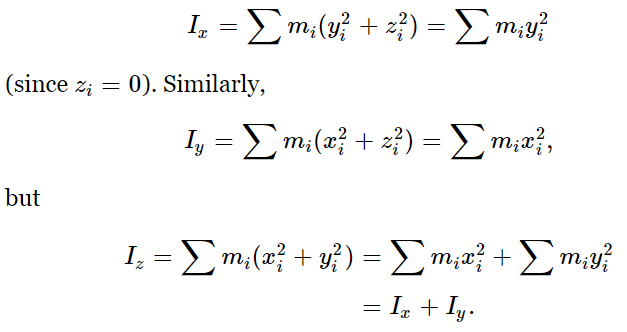
As an example, the moment of inertia of a uniform rectangular plate of mass M, width w, and length L, about an axis perpendicular to the plate and through its center is simply
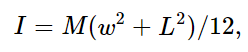
because its moment of inertia about an axis in its plane and parallel to its length is Mw2/12, i.e., just as for a rod of length w, and the moment of inertia about the other axis in its plane is ML2/12, just as for a rod of length L.
To summarize, the moment of inertia of an object about a given axis, which we shall call the z-axis, has the following properties:
3- The moment of inertia is
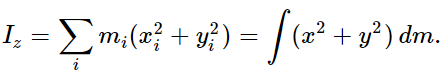
2- If the object is made of a number of parts, each of whose moment of inertia is known, the total moment of inertia is the sum of the moments of inertia of the pieces.
3- The moment of inertia about any given axis is equal to the moment of inertia about a parallel axis through the CM plus the total mass times the square of the distance from the axis to the CM.
4- If the object is a plane figure, the moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the plane is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia about any two mutually perpendicular axes lying in the plane and intersecting at the perpendicular axis.
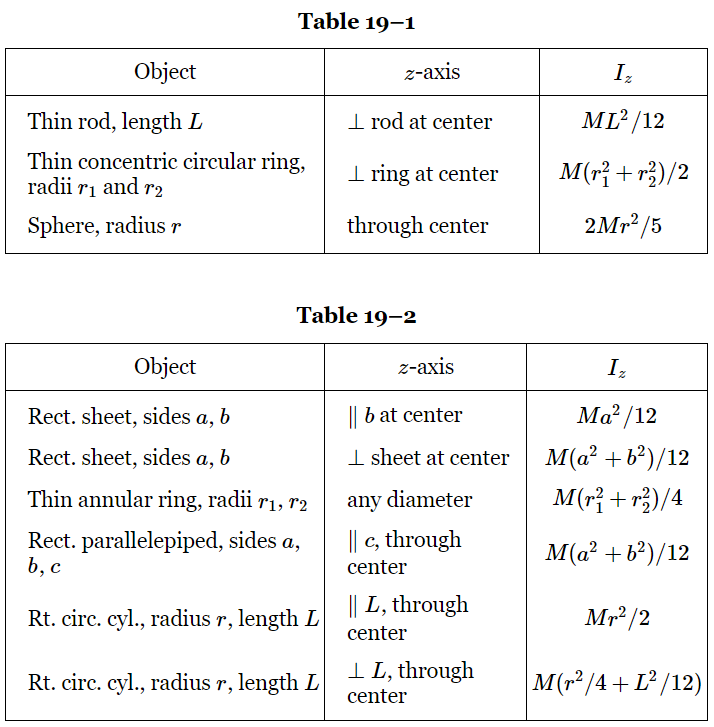
The moments of inertia of a number of elementary shapes having uniform mass densities are given in Table 19–1, and the moments of inertia of some other objects, which may be deduced from Table 19–1, using the above properties, are given in Table 19–2.



|
|
|
|
كيف تعزز نمو الشعر الصحي؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 فحوصات مهمة يجب القيام بها لسيارتك قبل الصيف
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم التربية والتعليم ينظّم جلسةً حوارية لملاكه حول تأهيل المعلّمِين الجدد
|
|
|
|
جامعة العميد تحدّد أهداف إقامة حفل التخرّج لطلبتها
|
|
|
|
جامعة العميد تحتفي بتخرّج الدفعة الثانية من طلبة كلّية الطبّ
|
|
|
|
قسم الشؤون الفكريّة يشارك في المؤتمر العلمي الدولي الخامس في النجف الأشرف
|