


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 5-1-2022
Date: 27-8-2021
Date: 8-10-2021
|
Amino acid isomers
Because the α-carbon of an amino acid is attached to four different chemical groups, it is an asymmetric (chiral) atom. Glycine is the exception because its α-carbon has two hydrogen substituents. Amino acids with a chiral α-carbon exist in two different isomeric forms, designated D and L, which are enantiomers, or mirror images (Fig. 1). [Note: Enantiomers are optically active. If an isomer, either D or L, causes the plane of polarized light to rotate clockwise, it is designated the (+) form.] All amino acids found in mammalian proteins are of the L configuration. However, D-amino acids are found in some antibiotics and in bacterial cell walls . [Note: Racemases enzymatically interconvert the D- and L-isomers of free amino acids.]
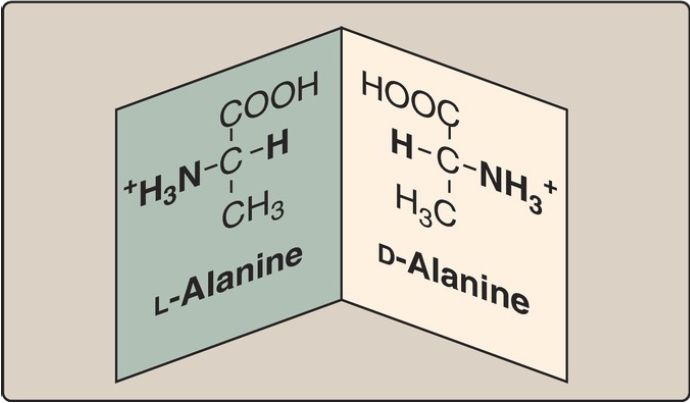
Figure 1. D and L forms of alanine are mirror images (enantiomers).

|
|
|
|
مقاومة الأنسولين.. أعراض خفية ومضاعفات خطيرة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمل جديد في علاج ألزهايمر.. اكتشاف إنزيم جديد يساهم في التدهور المعرفي ؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تقيم ندوة علمية عن روايات كتاب نهج البلاغة
|
|
|