

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
H Chains Are Assembled by Two Sequential Recombination Events
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
الجزء والصفحة:
29-4-2021
2073
H Chains Are Assembled by Two Sequential Recombination Events
KEY CONCEPTS
- The units for H chain recombination are a VH gene, a D segment, and a JH -CH gene segment.
- The first recombination joins D to JH -CH . The second recombination joins VH to DHJH -CH to yield VH -DHJH -CH .
- The CH segment consists of four exons.
The IgH locus includes an additional set of gene segments, the D segments. Thus, the assembly of a complete H chain entails recombination of VH , D, and JH genes. The D segment (for diversity) was discovered by the presence in the H chain peptide sequences of an extra 2 to 13 amino acids between the sequences coded by the VH and the JH segments. An array of D segments lies on the chromosome between the cluster of VH segments and that of JH segments.
VH DJH joining takes place in two stages (FIGURE 1). First, one of the D segments recombines with a JH segment; second, a VH segment recombines with the already recombined DJHsegment. The resulting VH DJH DNA sequence is then expressed with the nearest downstream CH gene, which consists of a cluster of four exons (the use of different CH genes is discussed in the section in this chapter titled Class Switch DNA Recombination). The D segments are organized in a tandem array. The human locus comprises about 30 D segments, followed by a cluster of 6 JH gene segments. The same D segment is involved in the DJH recombination and related VH DJH recombination.
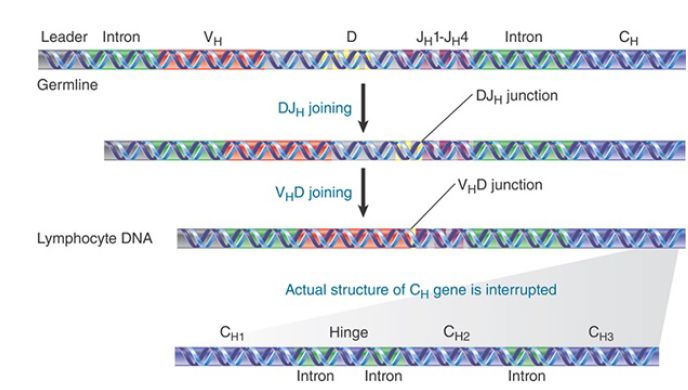
FIGURE 1. Heavy genes are assembled by sequential recombination events. First a DH segment is recombined with a JH segment, and then a VH gene segment is recombined with the DH segment.
The structure of recombined V(D)J segments is similar in organization in the H chain and λ and κ chain loci. The first exon codes for the signal sequence, which is involved in membrane attachment, and the second exon codes for the major part of the variable region itself, which is about 100 codons long. The remainder of the variable region is provided by the D segment (in the H chain locus only) and by a J segment (in all three loci).
The structure of the C region differs in different H and L chains. In both κ and λ chains, the C region is encoded by a single exon, which becomes the third exon of the recombined Vκ Jκ -Cκ or Vλ Jλ - Cλ gene. In H chains, the C region is encoded by multiple and discrete exons, separately coding for four regions: CH1; CH hinge; CH 2 and CH 3 (IgG, IgA, and IgD); or CH 1, CH 2, CH 3, and CH 4 (IgM and IgE). Each CH exon consists of about 100 codons, with the hinge exon being shorter; the intronic sequences are about 300 bp each.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















