

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Oxides and peroxides of group 2 metals
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Inorganic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p 283
19-1-2018
1619
Oxides and peroxides of group 2 metals
Beryllium oxide, BeO, is formed by ignition of Be or its compounds in O2. It is an insoluble white solid which adopts a wurtzite lattice. The oxides of the other group 2 metals are usually prepared by thermal decomposition of the corresponding carbonate.
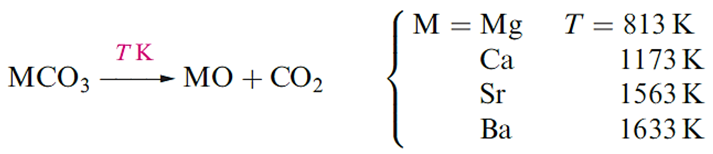
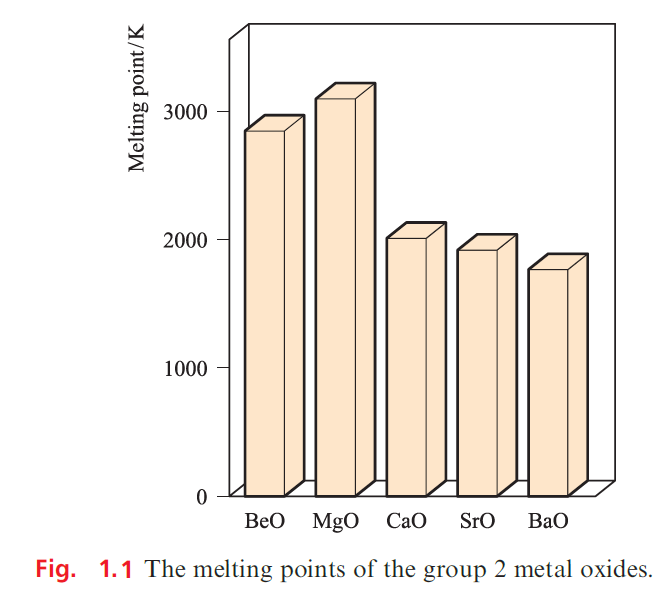
MgO, CaO, SrO and BaO crystallize with an NaCl lattice and the decrease in melting point reflects the decrease in lattice energy as the cation size increases . The high melting point of MgO makes it suitable as a refractory material.
Refractory materials are suitable for use in furnace linings; such a material has a high melting point, low electrical conductivity and high thermal conductivity, and is chemically inert at the high operating temperatures of the furnace. The action of water on MgO slowly converts it to Mg(OH)2 which is sparingly soluble. Oxides of Ca, Sr and Ba react rapidly and exothermically with water, and absorb CO2 from the atmosphere. The conversion of CaO to calcium carbide and its subsequent hydrolysis ( is industrially important although, as an organic precursor, ethyne is being superseded by ethene.
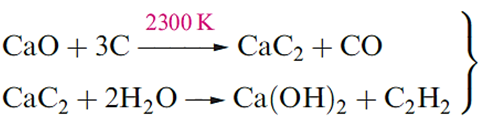
Group 2 metal peroxides, MO2, are known for M = Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba. Attempts to prepare BeO2 have so far failed, and there is no experimental evidence for any beryllium peroxide compound.† As for the group 1 metal peroxides, the stability with respect to the decomposition below reaction increases with the size of the M2+ ion. This trend arises from the difference between the lattice energies of MO and MO2 (for a given M) which becomes smaller as r increases; ΔlatticeHo(MO,s) is always more negative than ΔlatticeHo(MO2,s) .

All the peroxides are strong oxidizing agents. Magnesium peroxide (used in toothpastes) is manufactured by reacting MgCO3 or MgO with H2O2. Calcium peroxide is prepared by cautious dehydration of CaO2.8H2O.
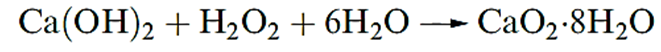
The reactions of SrO and BaO with O2 (600 K, 200 bar pressure, and 850 K, respectively) yield SrO2 and BaO2. Pure BaO2 has not been isolated and the commercially available material contains BaO and Ba(OH)2. Reactions of the peroxides with acids generate H2O2.

 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















