

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Catalytic cycles
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
ص691-693
2025-10-16
54
Catalytic cycles
Key point: A catalytic cycle is a sequence of reactions that consumes the reactants and forms products, with the catalytic species being regenerated after the cycle. The essence of catalysis is a cycle of reactions in which the reactants are consumed, the products are formed, and the catalytic species is regenerated. A simple example of a catalytic cycle involving a homogeneous catalyst is the isomerization of prop-2-en-1-ol (allyl alcohol (CH2CHCH2OH)) to prop-1-en-1-ol (CH3CHCHOH) with the catalyst [Co (CO)3H]. The first step is the coordination of the reactant to the catalyst. That complex isomerizes in the coordination sphere of the catalyst and goes on to release the product and reform the catalyst (Fig. 26.2). Once released the prop-1-en-1-ol tautomerises to propanal (CH3CH2CHO). As with all mechanisms, this cycle has been proposed on the basis of a range of information like that summarized in Fig. 26.3. Many of the components shown in the diagram were encountered in Chapter 21 in connection with the determination of mechanisms of substitution reactions. However, the elucidation of catalytic mechanisms is complicated by the occurrence of several delicately balanced reactions, which often cannot be studied in isolation. Two stringent tests of any proposed mechanism are the determination of rate laws and the elucidation of stereochemistry. If intermediates are postulated, their detection by magnetic resonance and IR spectroscopy also provides support. If specific atom-transfer steps
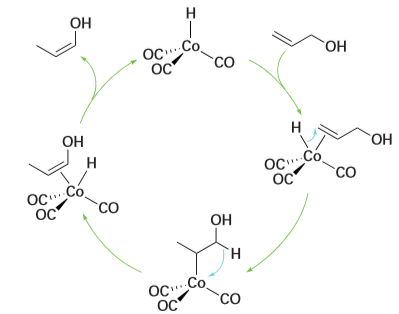
Figure 26.2 The catalytic cycle for the isomerization of prop-2-en-l-ol to prop-1-en-l-ol.
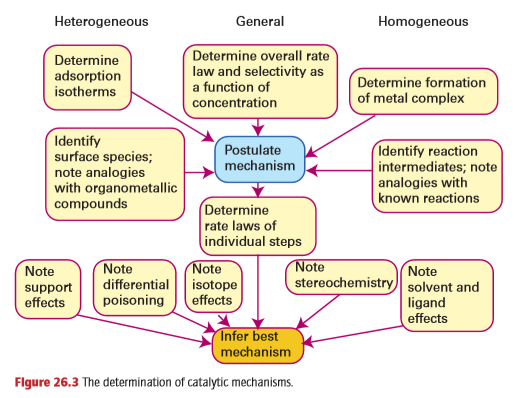
are proposed, then isotopic tracer studies may serve as a test. The influences of different ligands and different substrates are also sometimes informative. Although rate data and the corresponding laws have been determined for many overall catalytic cycles, it is also necessary to determine rate laws for the individual steps in order to have reasonable confidence in the mechanism. However, because of experimental complications, it is rare that catalytic cycles are studied in this detail.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















