

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous

Past Simple


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous

Passive and Active


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology


Semantics


Pragmatics

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies
European settlement of New England
المؤلف:
Naomi Nagy and Julie Roberts
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
270-15
2024-03-16
1124
European settlement of New England
Our story begins with the European settlement of a region that was previously populated by a variety of indigenous peoples. There has been no systematic study of the possible influences of the indigenous languages on English, but we can see their influence in local toponyms, for example the Piscataqua River in NH, the Kennebec River in ME, Lake Memphremagog in VT, and Contacook, a town in Rhode Island, as well as the word Massachusetts.
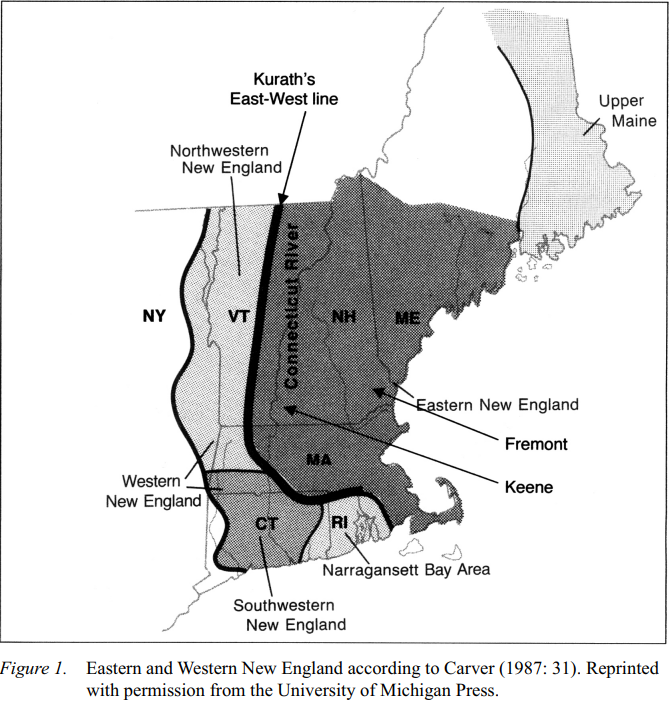
European settlers in Eastern New England came primarily from Boston, on the Massachusetts Bay, and were of English stock. This coastal area, originally home to indigenous groups, was settled by English immigrants in the early 1600’s and became one of the country’s cultural hearths. In search of better farm land, some of these original European settlers moved west from the coast and settled the Lower Connecticut River Valley in central CT. They were joined soon after by new immigrants from eastern and southern England, and later from Italy, Scotland and Ireland, among other places. Settlement spread, generally along river valleys, into NH, VT, ME, and RI (Carver 1987: 7).
WNE was settled by migration from central MA and central and western CT, including Hartford, Springfield, and New Haven, towns originally settled in the 1630s (Boberg 2001: 4). Following this movement, Eastern and Western NE remained isolated from each other until the early 18th century (Rosenberry 1962: facing 70; Kurath 1972: 42, cited in Boberg 2001: 4). Western VT was settled in the late 18th century by English-speaking migrants from western CT and MA (Kurath 1939-43: 104, cited in Boberg 2001: 5) and from NY (Rosenberry 1962: 136, cited in Boberg 2001: 5), as well as some settlers from east of the Green Mountains (NH, ME, and RI) (Kurath 1939-43: 103-4, cited in Boberg 2001: 5). WNE, in turn, was “the staging ground for the initial English-speaking settlement of the Inland North” (Boberg 2001: 9).
WNE also “received a considerable admixture of Scotch-Irish in the half century preceding the Revolution [early 18th century]” (Kurath 1928: 391, cited in Boberg 2001: 9), though they did not form a sizeable percentage of the population at any time. Also present in NE are Franco-Americans who moved south from French-speaking parts of Canada, and large Irish and Italian groups. Upper ME (north of Penobscot Bay) is quite distinct from the rest of the region, due to ties with New Brunswick, Canada (Carver 1987: 31).
Boston, the largest New England city, is still known as the hub, hearkening back to its position as the center from which settlements radiated in New England. Much of the rest of NE, however, is more rural, with many farms, forests, and undeveloped areas surrounding small towns and cities. Like many rural communities, NE is undergoing changes including increased highways, in-migration from other dialect areas, and change from small family farms to agribusiness (Frazer 1983; Labov 1994). The rural, regional dialects appear threatened with obsolescence due to the decrease in agriculture and increase in in-migration by speakers from other states. This loss evokes mixed reactions within the communities, where it may be seen as a sign of progress and increasing sophistication as well as a loss of cultural identity (Ring 1997).















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)

















