

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous

Past Simple


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous

Passive and Active


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs


Interjections

Express calling interjection


Grammar Rules

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology


Semantics


Pragmatics

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies
StAmE consonants
المؤلف:
William A. Kretzschmar, J
المصدر:
A Handbook Of Varieties Of English Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
267-14
2024-03-15
1234
StAmE consonants
There are only a few notable StAmE consonantal practices aside from the issue of postvocalic r already covered with the vowels in the previous section. The most prominent concern /t/. Intervocalic t is most often realized as a tap or flap, frequently with voicing, so that latter/ladder are homonyms for educated Americans, as 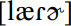 ; this pronunciation is transcribed as [lædər] in ODP, because the dictionary uses a restricted symbol set that does not include the
; this pronunciation is transcribed as [lædər] in ODP, because the dictionary uses a restricted symbol set that does not include the 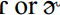 . /t/ is also frequently voiced prevocalically in consonant clusters such as –kt–, –pt–, –ft–, and –rt–. /t/ is typically deleted from –nt– clusters between vowels (unless separated by stress), for example making homonyms of the words winter/winner. The palatal glide /j/ remains firmly in place in words like cure, music, but in other words like Tuesday, coupon, neurotic it is frequently lost. Postvocalic /l/ is vocalized more and more often by educated speakers, except before juncture, to yield pronunciations like alcohol, milk
. /t/ is also frequently voiced prevocalically in consonant clusters such as –kt–, –pt–, –ft–, and –rt–. /t/ is typically deleted from –nt– clusters between vowels (unless separated by stress), for example making homonyms of the words winter/winner. The palatal glide /j/ remains firmly in place in words like cure, music, but in other words like Tuesday, coupon, neurotic it is frequently lost. Postvocalic /l/ is vocalized more and more often by educated speakers, except before juncture, to yield pronunciations like alcohol, milk 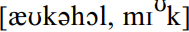 . Educated speakers sometimes voice other consonants as well, such as [εks-, εgz-] as variant pronunciations of the ex- prefix.
. Educated speakers sometimes voice other consonants as well, such as [εks-, εgz-] as variant pronunciations of the ex- prefix.















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاب (سر الرضا) ضمن سلسلة (نمط الحياة)

















